Overview

Intended Use
Collatamp®G is intended to be used during surgery to achieve haemostasis when blood comes into contact with the released tissue factors and exposed collagen fibrils.1 The adhesion and aggregation of platelets is induced on the collagen fibrils at the surface of Collatamp®G.1
Schematic representation of basement membrane and interstitial matrix localisation to the vascular wall2
The extracellular matrix surrounding the vascular vessel consists first of a basement membrane and then an interstitial matrix.
- Collagens of the basement membrane include collagen types IV, XV and XVIII.
- Collagens of the interstitial matrix include collagen types I, III and VI.
- The collagens provide tensile strength, adhesiveness, and structural integrity.
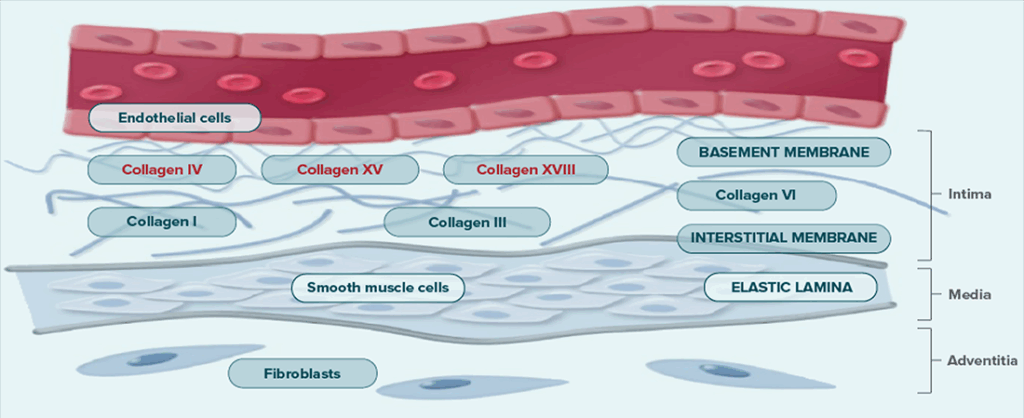
Adapted by SERB from Manon-Jensen T. et al. 2016

Local haemostasis
Haemostasis is triggered when blood comes into contact with released tissue factors and exposed endogenous collagen fibrils or renatured collagen fibrils like those in Collatamp®G. The adhesion and aggregation of platelets is induced on the renatured collagen fibrils of Collatamp®G and the plasmatic coagulation process is accelerated.1
The sponge-like structure of Collatamp®G stabilises the wound clot, and takes up a certain amount of blood. Collagen also promotes granulation and epithelialisation.1
The sponge-like structure of Collatamp®G stabilises the wound clot, and takes up a certain amount of blood. Collagen also promotes granulation and epithelialisation.1
References:
- Instructions For Use, Collatamp®G.
- Manon-Jensen T. et al., Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2016;14: 438-448.
- Wilhelm G, et al. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023;24(16):12563.